Duplex Modem¶
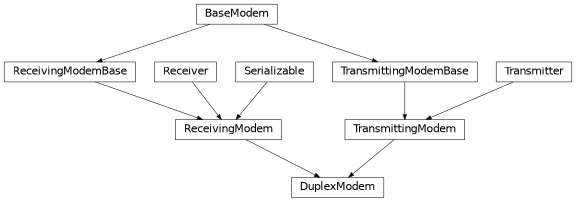
Duplex modems represent the signal processing chain of a communication device simulatenously transmitting and receiving information, implementing the digital signal processing before digital-to-analog conversion and after analog-to-digital conversion, respectively. They are a combination of a Transmitting Modem and a Receiving Modem.
After a DuplexModem is added as a
type of Transmitter to a Device,
a call to Device.transmit will be delegated
to TransmittingModemBase._transmit().
Similarly, after a DuplexModem is added as a
type of Receiver to a Device,
a call to Device.receive will be delegated
to ReceivingModemBase._receive()
1# Initialize a new simulation considering a single device
2simulation = Simulation()
3device = simulation.new_device(carrier_frequency=1e10)
4
5# Configure the link modeling the devices' transmit DSP
6modem = DuplexModem()
7device.add_dsp(modem)
8
9# Configure the links's waveform
10waveform = RootRaisedCosineWaveform(
11 oversampling_factor=4,
12 symbol_rate=1e6,
13 num_preamble_symbols=16,
14 num_data_symbols=32,
15 modulation_order=4,
16)
17modem.waveform = waveform
For a detailed description of the transmit and receive routines, refer to the Transmitting Modem and a Receiving Modem of the base classes.
The barebone configuration can be extend by additional components such as
Custom Bit Sources,
Synchronization,
TransmitSignalCoding,
ReceiveSignalCoding,
Channel Estimation,
TransmitSymbolCoding,
ReceiveSymbolCoding,
Channel Equalization and
Bit Encoders:
1# Configure a custom bits source for the modem
2modem.bits_source = RandomBitsSource(seed=42)
3
4# Configure the waveform's synchronization routine
5modem.waveform.synchronization = SingleCarrierCorrelationSynchronization()
6
7# Add a custom stream precoding to the modem
8modem.transmit_signal_coding[0] = ConventionalBeamformer()
9modem.receive_signal_coding[0] = ConventionalBeamformer()
10
11# Add a custom symbol precoding to the modem
12modem.transmit_symbol_coding[0] = DFT()
13modem.receive_symbol_coding[0] = DFT()
14
15# Configure the waveform's channel estimation routine
16modem.waveform.channel_estimation = SingleCarrierLeastSquaresChannelEstimation()
17
18# Configure the waveform's channel equalization routine
19modem.waveform.channel_equalization = SingleCarrierZeroForcingChannelEqualization()
20
21# Add forward error correction encodings to the transmitted bit stream
22modem.encoder_manager.add_encoder(RepetitionEncoder(32, 3))
23modem.encoder_manager.add_encoder(BlockInterleaver(192, 32))
- class DuplexModem(selected_transmit_ports=None, selected_receive_ports=None, carrier_frequency=None, bits_source=None, transmit_symbol_coding=None, receive_symbol_coding=None, transmit_signal_coding=None, receive_signal_coding=None, encoding=None, waveform=None, frame_generator=None, seed=None)[source]¶
Bases:
TransmittingModem,ReceivingModemRepresentation of a wireless modem simultaneously transmitting and receiving.
- Parameters:
selected_transmit_ports (
Optional[Sequence[int]]) – Indices of antenna ports selected for transmission from the operatedDevice'santenna array. If not specified, all available ports will be considered.selected_receive_ports (
Optional[Sequence[int]]) – Indices of antenna ports selected for reception from the operatedDevice'santenna array. If not specified, all available ports will be considered.carrier_frequency (
float|None) – Carrier frequency of the transmitted and received communication signals.bits_source (
BitsSource|None) – Source configuration of communication bits transmitted by this modem. Bits are randomly generated by default.transmit_symbol_coding (
Union[TransmitSymbolCoding,Sequence[TransmitSymbolEncoder],None]) – Complex communication symbol coding configuration during transmission.receive_symbol_coding (
Union[ReceiveSymbolCoding,Sequence[ReceiveSymbolDecoder],None]) – Complex communication symbol coding configuration during reception.transmit_signal_coding (
Union[TransmitSignalCoding,Sequence[TransmitStreamEncoder],None]) – Stream MIMO coding configuration during signal transmission.receive_signal_coding (
Union[ReceiveSignalCoding,Sequence[ReceiveStreamDecoder],None]) – Stream MIMO coding configuration during signal reception.encoding (
Union[EncoderManager,Sequence[Encoder],None]) – Bit coding configuration.waveform (
CommunicationWaveform|None) – The comminication waveform to be transmitted and received by this modem.frame_generator (
FrameGenerator|None) – Frame generator used to pack and unpack communication frames.seed (
int|None) – Seed used to initialize the pseudo-random number generator.
- classmethod Deserialize(process)[source]¶
Deserialize an object’s state.
Objects cannot be deserialized directly, instead a
Factorymust be instructed to carry out the deserialization process.- Parameters:
process (
DeserializationProcess) – The current stage of the deserialization process. This object is generated by theFactoryand provides an interface to deserialization methods supporting multiple backends.- Return type:
- Returns:
The deserialized object.
- serialize(process)[source]¶
Serialize this object’s state.
Objects cannot be serialized directly, instead a
Factorymust be instructed to carry out the serialization process.- Parameters:
process (
SerializationProcess) – The current stage of the serialization process. This object is generated by theFactoryand provides an interface to serialization methods supporting multiple backends.- Return type: